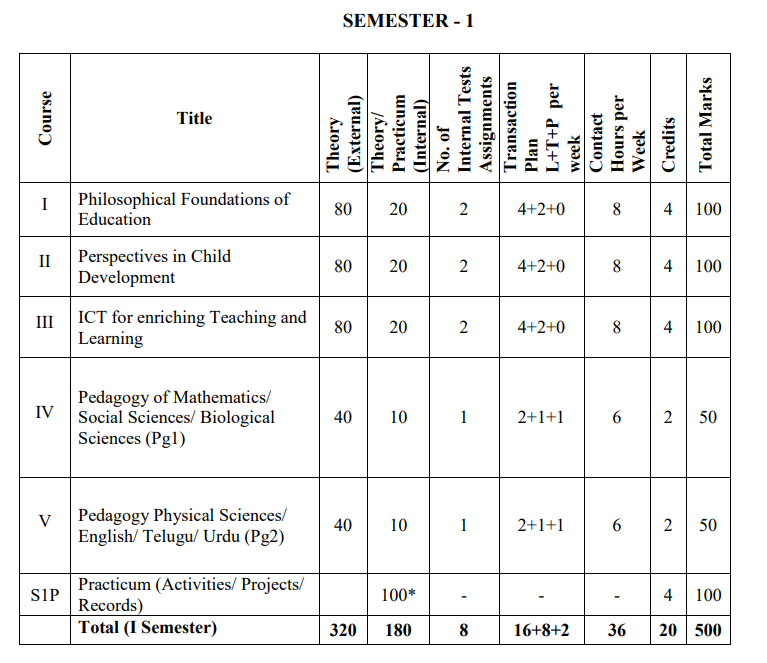
Andhra Pradesh B.Ed Syllabus for 1st Semester
Subject-I: Philosophical Foundations of Education
Unit-1: Introduction to Philosophy and Education
1.1 Understanding the Concept and Scope of Philosophy
1.2 Understanding the Concept and Scope of Education
1.3 Types and Functions of Education
1.4 The Relationship between Philosophy and Education
1.5 Philosophy and the Aims of Education
Unit-2: Indian Education – A Historical Overview
2.1 Education in the Ancient Period (Vedic, Buddhist, and Jain Education)
2.2 Education in the Medieval Period (Including Islamic Education)
2.3 Education in the Modern Period (Pre- and Post-Independence Era)
- i. Rabindranath Tagore
- ii. Sri Aurobindo Gosh
- iii. Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi
- iv. Jiddu Krishnamurti
- v. Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
- vi. Maulana Abul Kalam Azad
Unit-3: Eastern Philosophical Systems and Western Schools of Philosophy
3.1 Eastern Philosophical Systems
- i. Sankhya
- ii. Yoga
- iii. Nyaya
- iv. Vedanta
3.2 Western Schools of Philosophy - i. Idealism
- ii. Naturalism
- iii. Pragmatism
- iv. Existentialism
Unit-4: Value Education
4.1 Concept of Values
4.2 Classification of Values
4.3 The Crisis of Values
4.4 Approaches to Inculcating Values
4.5 Values and Harmonious Living
Unit-5: Teaching as a Profession
5.1 Professional Competencies and Commitments of Teachers
5.2 The Teacher as a Nation Builder
5.3 The Teacher as a Creator and Facilitator of Knowledge
5.4 Professional Ethics for Teachers
5.5 The Teacher’s Role in Shaping the Future Society
Subject-II: Perspectives in Child Development
Unit-1: Approaches to Human Development
1.1 Concept of Growth, Development, and Maturation
1.2 Principles of Development
1.3 Stages of Growth and Development (Infancy, Childhood, Adolescence)
1.4 Dimensions of Growth and Development (Physical, Cognitive, Emotional, Social, Moral, Language)
1.5 Longitudinal and Cross-Sectional Approaches to Understanding Development
Unit-2: Theories of Development
2.1 Piaget’s Cognitive Development Theory
2.2 Erikson’s Psychosocial Development Theory
2.3 Kohlberg’s Moral Development Theory
2.4 Freud’s Psychosexual Development Theory
2.5 Goleman’s Emotional Development Theory
Unit-3: Childhood as a Period of Socialization
3.1 Characteristics and Developmental Tasks of Childhood
3.2 Physical, Cognitive, Social, Emotional, Moral, and Language Development in Childhood
3.3 The Child in Different Socio-Cultural Contexts
3.4 The Process of Socialization – Conflict Resolution and Social Development
3.5 Stages of Social Development – Isolated Play, Parallel Play, and Social Play; Characteristics of Socially Mature Individuals
Unit-4: Adolescence as a Period of Transition
4.1 Characteristics and Needs of Adolescence
4.2 The Origins of Problems During Adolescence – Physical, Cognitive, Emotional, Social, Moral, and Language Development
4.3 Adolescent Groups – Gangs
4.4 Adjustment Mechanisms with a Focus on Defense Mechanisms and Holistic Development
4.5 Leadership: Types of Leadership, Development of Leadership Qualities in Adolescents, and Educational Implications
Unit-5: Individual Differences
1.1 Dimensions of Individual Differences – Cognitive Abilities, Interests, Aptitude, Creativity, Personality, and Values
1.2 Gardner’s Theory of Multiple Intelligences – Implications for Understanding Differences in Children
1.3 Differences Among Children Based on Learning Styles and Socio-Cultural Context (Home Language vs. Instructional Language)
1.4 Individual Differences in Cognitive Abilities – Learning Difficulties, Slow Learners, Intellectually Challenged, Intellectually Gifted – Implications for Addressing Individual Variations from a “Differences” Rather than “Deficits” Perspective
1.5 Encouraging Creativity in Children
Subject-III: Information and Communication Technology (ICT) for Enriching Teaching and Learning
Unit-1: Information and Communication Technology (ICT)
1.1 Educational Technology – Concept, Growth, Objectives, Characteristics, Advantages, Challenges, and Impact
1.2 Information Technology – Knowledge Explosion, Preservation, and Retrieval
1.3 Communication – Concept, Elements, Process, Barriers & Types; Teaching as Communication – Communication Technology and Its Application in Education
1.4 Instructional Media and Aids – Aural, Print, Visual, and Multimedia
1.5 The Concept, Importance, Characteristics, and Scope of Information and Communication Technology (ICT)
Unit-2: ICT in Education
2.1 Knowledge Acquisition and Multi-Sensory Approaches
2.2 Classroom Communication and Communicative Skills for Teachers and Students – Flanders Interaction Analysis Category System
2.3 Individualized Instruction – Concept, Need, Principles, and Techniques
2.4 Programmed Learning – Principles, Types, Modes of Presentation, Development, Application, and the Role of the Teacher
2.5 The Evolving Roles of Learners and Teachers in ICT Integration and the Associated Challenges
Unit-3: Computer Fundamentals and Applications
3.1 Types, Characteristics, and Features of Computers
3.2 Components of Computers – Hardware, Software, Memory, and Maintenance
3.3 Operating Systems – DOS, Windows, Macintosh, and Mobile Apps for Teaching
3.4 Software for Word Processing, Presentations, Statistical & Graphical Applications, Page Layout, Multimedia, and Webpage Creation
3.5 The Concept, Applications, and Challenges of Computer Networks, the Internet, Email, and Digital Space
Unit-4: ICT-Enriched Learning Experiences
4.1 The Application of ICT for Enriching Classroom Experiences
4.2 Using Multimedia Educational Software in the Classroom
4.3 Leveraging Internet-Based Media for Teaching and Learning Enrichment
4.4 Project-Based Learning Utilizing Computers, the Internet, and Related Activities
4.5 Collaborative Learning Through Group Discussions, Projects, Field Visits, Blogs, etc.
Unit-5: Application of Computers in Education
5.1 Computers as Learning Tools – The Concept of E-Learning
5.2 Web 2.0 Technologies – Characteristics, Types, and Examples
5.3 Virtual Classrooms, Smart Boards, Tools, and Opportunities
5.4 Open Educational Resources – Concept and Significance
5.5 Critical Issues in Internet Usage – Authenticity, Addiction, Plagiarism, Ethical and Legal Standards
Subject-IV: Pedagogy of Mathematics
Unit-1: Meaning, Nature, and Scope of Mathematics
1.1 Understanding the Meaning, Nature, and Scope of Mathematics
1.2 The History of Mathematics with a Focus on Teaching Mathematics
1.3 Contributions of Indian Mathematicians: Aryabhatta, Brahmagupta, Varahamihira, Bhaskaracharya, Srinivasa Ramanujan
1.4 Contributions of Western Mathematicians: Euclid, Pythagoras, René Descartes, George Cantor
1.5 Correlating Mathematics with Other School Subjects and Various Branches of Mathematics
Unit-2: Aims and Objectives of Teaching Mathematics
2.1 The Need for Establishing General Objectives in Teaching Mathematics
2.2 The Aims, Values, and General Objectives of Teaching Mathematics
2.3 Specific Objectives and Teaching Points Across Various Content Areas in Secondary School Mathematics
2.4 Recommendations from Various Educational Committees and Commissions Regarding the Aims and Objectives of Teaching Mathematics
2.5 Understanding the Concept of Academic Standards in CCE
2.6 Linking Bloom’s Taxonomy with Academic Standards
Unit-3: Methods, Approaches, and Strategies in Teaching and Learning Mathematical Concepts
3.1 Understanding the Nature of Concepts, Types of Concepts, Concept Formation, and Assimilation; Distinguishing and Stating Necessary and Sufficient Conditions in the Process of Teaching Concepts; Comparing and Contrasting; Using Counterexamples and Non-Examples; Planning and Implementing Strategies in Teaching Concepts
3.2 Raising Awareness Among Student Teachers About Various Concepts in Arithmetic, Algebra, Geometry, Trigonometry, Probability, and Statistics from Classes VI to X
3.3 Methods of Teaching Mathematics: Inductive and Deductive Approaches, Analytic and Synthetic Methods, Laboratory, Heuristic, Project Method, and Activity-Based Teaching
3.4 Problem Solving – Stages and Steps in Problem Solving; Discovering or Exploring Various Options for Solving Problems in Algebra, Arithmetic, Geometry, Trigonometry, Probability, and Statistics
3.5 Jerome Bruner’s Concept Attainment Model
Unit-4: Planning for Teaching-Learning Mathematics
4.1 Microteaching: Concept, Definition, Microteaching Cycle, Components of Microteaching, Merits, and Limitations
4.2 Microteaching Skills: Introducing a Lesson, Explaining a Concept, Stimulus Variation, Illustrating with Examples, Probing Questions, Reinforcement, Structuring Classroom Questions, Blackboard Writing
4.3 Planning Instruction: Unit Plan, Period Plan Based on Bloom’s Taxonomy and Academic Standards
4.4 Technology-Integrated Lesson Planning
Unit-5: Learning Resources in Mathematics
1.1 The Importance and Criteria for a Good Mathematics Textbook
1.2 A Critical Analysis of Existing Secondary School Mathematics Textbooks
1.3 Selecting and Designing Audio, Visual, and Multimedia Resources
5.4 Online Resources – ICT-Based Pedagogical Tools
5.5 Utilizing Community Resources for Mathematics Learning; Visits, Mathematical Field Trips, and Excursions
5.6 Overcoming Challenges in Utilizing Resources
Course-IV: Pedagogy of Social Sciences
Unit-1: Social Sciences as an Integrated Area of Study
1.1 Understanding the Meaning, Nature, and Scope of Natural and Social Sciences
1.2 The Distinction Between Natural and Social Sciences
1.3 The Meaning, History, Nature, Scope, and Development of Social Studies
1.4 The Distinction Between Social Sciences and Social Studies
1.5 Understanding Society Through Various Social Sciences
Unit-2: Aims, Objectives, and Academic Standards of Social Sciences
2.1 Major Aims and Objectives of Teaching Social Sciences
2.2 Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives
2.3 Academic Standards and Learning Outcomes in Social Sciences Education
2.4 Recommendations from NPE 1986, NCF 2005, and APSCF 2011
2.5 The Values of Teaching Social Sciences
Unit-3: Approaches, Methods, Strategies, and Techniques of Teaching Social Sciences
3.1 Understanding the Need and Significance of Various Approaches, Methods, Strategies, and Techniques in Teaching Social Sciences
3.2 Teacher-Centered Approaches: Lecture, Lecture-Demonstration, Source, and Supervisory Study
3.3 Learner-Centered Approaches: Project, Problem Solving, Discussion, Inductive and Deductive, Observation, Constructivist Approach
3.4 Strategies/Techniques: Brainstorming, Team Teaching, Mind Mapping, Questioning
3.5 Activities: Dramatization, Role Play, Field Trips, Social Science Clubs, Exhibitions
Unit-4: Planning in Teaching Social Sciences
4.1 Microteaching – Concept and Steps
4.2 Microteaching Skills: Introduction, Explanation, Questioning, Reinforcement, Stimulus Variation
4.3 Year Plan and Unit Plan
4.4 The Need and Importance of Lesson Planning (Period Planning)
4.5 Technology-Integrated Lesson Planning
Unit-5: Teaching-Learning Resources in Social Sciences
5.1 Community Resources – Human and Material
5.2 Social Science Libraries, Laboratories, and Museums
5.3 The Need and Significance of Current and Controversial Issues in Social Sciences Education
5.4 Overcoming Challenges in Utilizing Resources
5.5 Professional Development of Social Sciences Teachers
Subject-IV: Pedagogy of Biological Sciences
Unit-1: Introduction to Science
1.1 The Meaning and Functions of Science
1.2 The Nature and Scope of Science
1.3 The Structure of Science
1.4 Branches of Science
1.5 The History of Biological Science
Unit-2: Aims and Values of Biological Science
2.1 The Aims of Teaching Biological Science
2.2 The Values of Teaching Biological Science
2.3 Competencies of a Biological Science Teacher
2.4 Correlating Biological Science with Other School Subjects
Unit-3: Objectives of Teaching Biological Science
3.1 Understanding the Meaning and Importance of Objectives
3.2 Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives
3.3 Instructional Objectives and Specifications with Examples
3.4 Academic Standards in School Biological Science Textbooks Published by the Government of Andhra Pradesh
Unit-4: Methods and Techniques of Teaching Biological Science
4.1 Microteaching Techniques
4.2 Lecture Method, Lecture Demonstration Method, and Laboratory Method
4.3 Scientific Method (Inductive and Deductive Methods)
4.4 Project Method
Unit-5: Planning for Teaching Biological Science
5.1 Year Plan
5.2 Lesson Plan
5.3 Period Plan (Herbartian and Constructivist Approach and CCE Model)
5.4 Learning Experiences
5.5 Planning ICT Applications in Learning Biology
Subject-V: Pedagogy of Physical Sciences
Unit-1: Introduction to Science and Physical Sciences
1.1 Science and Physical Sciences – Meaning, Nature, Scope, and Importance
1.2 The Structure of Science – Syntactic Structure (Process of Science – Domain of Inquiry), Substantive Structure (Product of Science – Facts, Concepts, Theories, Laws, and Principles) with Examples from Physical Sciences
1.3 The Values of Learning Physical Sciences
1.4 Correlating Physical Sciences with Mathematics, Biological Sciences, Social Studies, Languages, Fine Arts, Environment, Health, Development, Peace, and Equity
1.5 Analysis of Selected Concepts in Physics and Chemistry from Classes 6-10
Unit-2: Development of Science – Physical Sciences
2.1 Milestones in the Development of Science – Physics and Chemistry
2.2 Contributions of Western and Indian Scientists
2.3 Landmarks, Status, and Development of Indian Science and Technology
2.4 The Role of Physical Science in Human Life
2.5 The Rationale for Inspiring Students to Study Physical Science
Unit-3: Aims, Objectives, and Competencies in Teaching Physical Sciences
3.1 The Aims and Objectives of Teaching Physical Sciences
3.2 Taxonomy of Educational Objectives – Bloom, Krathwohl, Simpson, et al; Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy and Higher Order Thinking Skills
3.3 Instructional Objectives in Teaching Physical Sciences
3.4 Behavioral or Specific Objectives in Teaching Physical Sciences
3.5 Competencies for Teaching Physical Sciences
Unit-4: Approaches, Methods, and Techniques of Teaching Physical Sciences
4.1 The Concept of Teaching with a Focus on Physical Science – Approaches and Methods; Student Participation in Learning
4.2 Teacher-Centered Methods: Lecture, Lecture-Demonstration, Historical Approaches
4.3 Student-Centered Methods: Heuristic, Project, Scientific, and Laboratory Methods (Illustrations from Specific Content in Physics and Chemistry)
4.4 Modern Teaching Techniques: Brainstorming, Team Teaching, Concept Attainment Model, and Inquiry Training Model
4.5 Microteaching: Concept, Meaning, Microteaching Skills, and Practice
Unit-5: Planning for Teaching Physical Sciences
5.1 The Importance of Planning in Teaching
5.2 Year Plan
5.3 Unit Plan
5.4 Period Plan (Lesson Plan) – Herbertian Steps vs. Constructivist Approach
5.5 Teaching Strategies and Academic Standards, CCE Model Period Plan for Classroom Teaching
Subject-V: Pedagogy of English
Unit-1: Introduction to English Language Teaching (ELT)
1.1 The Meaning, Nature, and Scope of ELT
1.2 The Status of the English Language in Global and Indian Contexts
1.3 Aims and Objectives of Teaching English in India
1.4 Language and Education Policy in India
1.5 Teaching English in Bilingual/Multilingual Contexts
Unit-2: Methods and Approaches in ELT
2.1 Method, Approach, and Technique
2.2 Grammar-Translation Method, Direct Method, Bilingual Method, and Dr. West’s Method
2.3 Oral, Situational, and Structural Approaches
2.4 Communicative Language Teaching
2.5 Micro Skills in ELT
Unit-3: Listening and Speaking Skills
3.1 Types and Sub-Skills of Listening
3.2 Techniques and Materials for Teaching Listening
3.3 Sub-Skills of Speaking
3.4 Techniques and Materials for Teaching Speaking
3.5 Activities for Developing Listening and Speaking Skills
Unit-4: Reading and Writing Skills
4.1 Types and Sub-Skills of Reading; Methods of Teaching Reading
4.2 Reading and Reflecting on Texts
4.3 Mechanics of Writing
4.4 Sub-Skills and Techniques of Writing
4.5 Activities for Developing Reading and Writing Skills
Unit-5: Developing Integrated Skills and Using ICT in English Language Teaching
5.1 Teaching of Prose
5.2 Teaching of Poetry
5.3 The Use of Multimedia in ELT
5.4 Online Resources for ELT
5.5 ELT and Social Networking