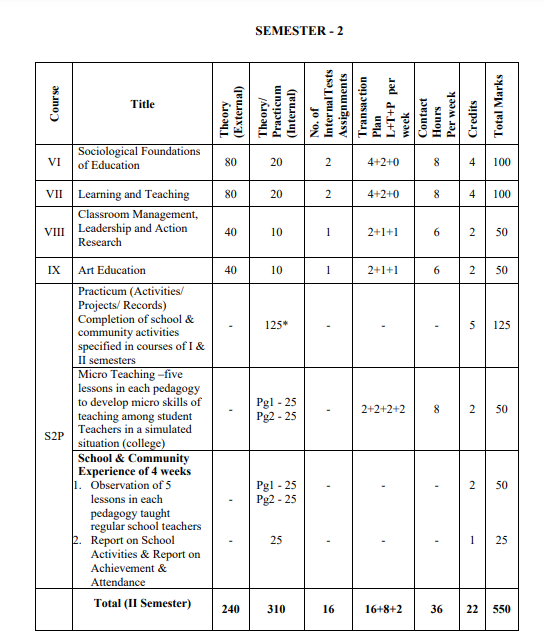
VI : SOCIOLOGICAL FOUNDATIONS OF EDUCATION
Objectives
After completion of the course, the student-teacher will be able to
- understand the sociological basis of Education
- understand the impact of culture and socialization on Education
- sensitize the student teacher about the impact of Education on the quality of life
- understand the preamble of the constitution in the light of Education
- organize various programmes to achieve national integration and international understanding
Course Content
Unit-1: Sociology and Education
- Meaning, nature and scope of sociology
- Relationship between sociology and Education
- Agencies of socialization (Family, peer group, school, Media, Religion
- Role of Teacher in Socialisation process
- Impact of Socialisation on Education
Unit-II: Culture and Education
- Meaning and definitions of culture
- Characteristics of culture
- Dimensions of culture, cultural lag, cultural pluralism
- Impact of culture on Education
- Role of Education in preservation, transmission and promotion of culture
Unit-III: Social Change and Education
- Meaning and factors responsible for Social change
- Concept and attributes of Modernization
- Social stratification, Social Mobility and Education
- Education as a facilitator for social change
- Social Networking its implications on social cohesion and education
Unit-IV: Democracy and Education
- Concept and Principles of Democracy
- Equality and equity in Education
- Preamble of the Constitution in relation to Education
- Role of Education in strengthening democracy and democratic citizenship Teacher as a democrat
Unit-V: Education and National Integration
- Concept, Need for National Integration
- Education as an instrument for national integration
- Programmes to promote National Integration and International understanding,
- Peace education in schools
- Social Crisis and its Management
Activities
- Study the cultural practices prevailing in the local community and submit a report
- Study the diversities existing in the community and describe the root causes for such
- Study the social stratification in a village/ward and prepare a report on
- Education and social mobility – Conduct a survey in a village/ward and prepare a report
VII: LEARNING AND TEACHING
Objectives
- After completion of the course, the student-teacher will be able to
- To be aware of the process of learning and information processing
- To gain an understanding of different theoretical perspectives on learning
- To reflect on their own implicit understanding of the nature and kinds of learning
- To explore the possibilities of designing learning environment and experiences at school
- To appreciate the critical role of learner differences and social contexts in making meanings and drawing implications for schools and teachers
Course Content
Unit-1: Process of Learning
- Concept of learning, types of learning and factors influencing learning
- Learning process: Attention, sensation, perception, and concept formation
- Memory & forgetting: concept, types of memory, applicability to learning and strategies for better management of memory.
- Transfer of learning: concept, theories and types( Horizontal and Vertical)
- Role of motivation in learning; methods of improving motivation
Unit-2: Behaviorist Perspectives of Learning
- Trial and error – Thorndike, Laws of learning, concept and principles and classroom implications
- Classical Conditioning – Pavlov, concept and principles and classroom implications
- Operant Conditioning – Skinner, concept and principles and classroom implications
- Compare these perspectives in terms of their merits and applicability to classroom learning
Unit-3: Cognitive and Humanist Perspectives of Learning
- Cognitive perspectives of learning (insight learning – Kohler, Discovery learning – Bruner, Developmental theory of learning – Piaget, Social Learning – Bandura, constructivism – Vygotsky)
- Humanist perspectives of learning (Learner centered approach – Rogers)
Unit-4: Teaching Process
- Concept of teaching, teaching as a profession and teacher as a professional, teaching as an art and science
- Distinction between Instruction, training and teaching
- Phases of teaching: planning, execution and reflection
- Role of teacher in teaching learning process: teacher as a model, facilitator, negotiator, co-learner, reflective practitioner and classroom researcher
- Functions of a teacher in classroom, school and community
Unit-5: Learning Environment and Learning Engagement
- Meaning of learning environment and learning engagement
- Creating positive and productive environment for learning – creation of emotionally safe learning environment to increase learning
- Development of emotional intelligence
- Role of culture in the educative process, creating culturally responsive learning environment, create cultural congruity between home and school
- Assisted performance, supervised discussion and reciprocal teaching as strategies to enhance motivation and learning
Activities
- Prepare a list of study habits prevailing among students of a particular class through interaction of students
- A report on learning situations, learners attention, motivational status among the students of a particular class through observation
- Conduct a group discussion on strategies of memorization – Repeated reading, writing, peer group discussion, explaining to others, and prepare a report
- Understanding the nature of interaction between teachers and students by Flander‟s
Interaction model and prepare a report
VIII: CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT LEADERSHIP AND ACTION RESEARCH
Objectives
- After completion of the course, the student-teacher will be able to
- understand the importance of classroom organization
- understand the importance of classroom Management
- develop ability to face the problems in managing the
- understand the role of leadership of a teacher
- undertake different action research projects to improve professional practices
Course Content
Unit-1: Classroom Organization
- Classroom organization – Meaning and purpose
- Classroom Seating Arrangement for different purposes
- Technology integration – OHP/ LCD, Smart board, Chalk board, White board, Display boards, multimedia, E-Classroom.
- Characteristics of Classroom Environment – Learner friendly and inclusive
- Management and maintenance of physical and material resources to optimize access to learning; Sharing of resources – School Complex
Unit-2: Classroom Management
- Classroom management – concept, need and approaches .
- Managing with different types of students – Leader, Follower, passive
- Classroom behavior management – problems, mistakes, disciplinary practices, corporal punishments, classroom rules, routines and regulations.
- Violation of rights of children – legal
- Strategies to manage behavior problems- preventive, supportive and
- Time management in a classroom – Allocated time, instructional time, engaged time and Academic learning
Unit-3: Role of Teacher in School Functions
- Teacher as a facilitator of learning
- Perspective planning and coordination with authorities for
- Accountability and self assessment of teachers and feedback
- Conducive school environment – team work, transparency, self esteem among head teacher, teachers,
Unit-4: Teacher as a Leader
- Concept, Nature and Characteristics of a Leader
- Types of Leadership
- Strategies to develop leadership qualities
- Role of a teacher as a leader in managing classroom dynamics
Unit-5: Action Research in Education
- Action Research – Meaning, Need and Scope
- Steps in Action Research
- Action Research Cycle
- Action Research Problem Areas – Student, Classroom, School, Teacher, Administration, etc.
Activities
- Prepare a detailed record describing the role of the teacher in organizing the classroom at least by observing a teacher for five periods.
- Identify a problem for action research and prepare a proposal for action research
- Collection of articles from newspapers relating to classroom management problems
- Collection of cases of indiscipline and corporal punishment from newspapers
- Observe a minimum of five school teachers and describe their leadership characteristics Text
IX: ART EDUCATION
Objectives
- After completion of the course, the student-teacher will be able to
- integrate Art with Education and become better
- develop creative thinking through different Art
- realize that liberal arts help in making better
- understand Art as a medium of
- understand the role of Art as a medium of
- deepen students ability for perception and
- use Art as an alternative languages to experience and communicate concepts in teaching-learning.
Course Content
Unit-1: Art and Aesthetics
- Aesthetics – as a branch of
- Aesthetics – its meaning, dimensions and
- Art as a form of
- Indian Art and Rasa
- Importance of Arts in Education
Unit-2: Art and Education
- Art as a medium of
- Art as a unifying principle in
- Art and
- Art and Human
- Art for self- expression, keen observation, and sense of
Unit-3: Place of Visual Art and Performing Arts in Teaching
- Different forms of visual and performing
- Teaching as an
- Drama as a form of
- Identification of local Art forms and their integration to teaching –
- Evaluation strategies; assessing the different forms of
Unit-4: Contributions made by Contemporary thinkers on Art and Education
- Rabindranath Tagore
- K. Coomara Swamy
- Herbert Read
- Elliot Eisener
Unit-5: Art and Craft in Education
- Art in Craft
- Craft in Art
- Traditional Craft and their relevance to Education
- Local Craft and their place in SUPW
- Indian Festivals and its Artistic significance
Activities
- Select a concept from the school curriculum which includes a social message and identify an appropriate art form to spread the message in public and prepare a report
- Identify a local art form and integrate it in teaching an appropriate lesson from school curriculum – Prepare a lesson plan
- Select an appropriate lesson from the school curriculum and rewrite it in the form of a drama